 What a conventional name this oil has! The name ‘Sugandha Kokila’ sounds like a typical Indian name concealing a handful of health benefits in it. And I am not wrong; ‘Sugandha’ is a Sanskrit name meaning ‘Fragrant’.
What a conventional name this oil has! The name ‘Sugandha Kokila’ sounds like a typical Indian name concealing a handful of health benefits in it. And I am not wrong; ‘Sugandha’ is a Sanskrit name meaning ‘Fragrant’.
The unique, rich, herbaceous, warm, camphoraceous and spicy aroma of Sugandha Kokila essential oil is extracted from the dried berries of this plant, scientifically known as Cinnamomum glaucescens is a member of the Lauraceae family. The ancient Ayurvedic texts recommend the use of this oil as a natural tonic for the digestive system and the central nervous system.
Purchase Sugandha Kokila Essential Oil – Wholesale – CLICK HERE
This is an evergreen tree native to the tropical Himalayan regions in Nepal, Bhutan and India (Khasi Hills, Sikkim and Manipur). Sugandha Kokila tree is locally known as Gondsoroi and Malligiri and Cinnamon berry is its common name. This large-sized tree has the potential to grow in plains as well as hilly areas up to an average altitude of 1500m.
The major constituents and therapeutic properties:
Experts say that the constituents of this oil belong to the chemical family of monoterpenes, esters and oxides. The principal constituents responsible for the remedial properties of this oil are a-pinene, ß- pinene, camphor, sabinene, eucalyptol, a- terpineol, 1,8-cineole, ß-phellandrene (trace), ß–myrcene, p-Cymene, linalool and trans methyl cinnamate.
The therapeutic values of Sugandha Kokila essential oil are digestive, anti-arthritic, carminative, analgesic, antiseptic, relaxant, stomachic, antimicrobial, emmenagogue, astringent and antibiotic.
Ayurvedic health benefits of Sugandha Kokila oil:
Ayurveda is an optimistic curative methodology that considers illness as an opportunity for healing and as the right time for change. Being the oldest medicinal system, Ayurveda trusts that good health is the harmony between one’s physical, mental and spiritual wellness depending upon his/her diet, lifestyle and certain other environmental factors.
Ayurvedic approach towards health is highly accepted for its simple treatment techniques using natural medications like herbs and essential oils along with exercises, yoga, meditation, lifestyle changes and the art of balanced living.
Essential oils are the vital life force of plants as they transform the real energy of the plants from which they are extracted. Ayurveda believes that this vital energy of plants will highly help in increasing the prana or life force of human beings when used in an appropriate manner. Essential oils are said to strengthen the sense of smell, the predominant one among the five senses.
The aromatic molecules of the essential oils reach the limbic system of the brain through the nasal passage, where limbic system is the control center that is responsible for feelings, emotions and certain other functions of the body. Using essential oils in Abhyanga or the art of Ayurvedic massaging grant ultimate relief by entering into the bloodstream gradually.
Sugandha Kokila essential oil, for its matchless aroma and incredible healing values is called as ‘A Gift to Perfumers from the Himalayan Kingdom of Nepal’.
The most important Ayurvedic health benefits of this oil are:
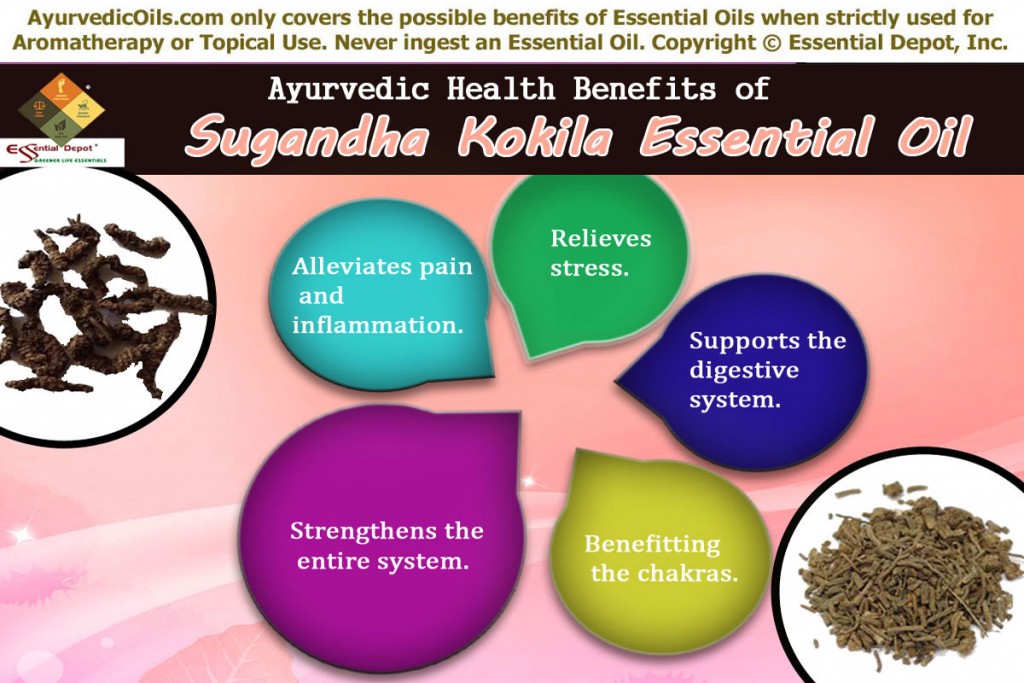 1. Alleviates pain and inflammation:
1. Alleviates pain and inflammation:
Sugandha Kokila essential oil is a natural analgesic that deadens pain. It aids in enhancing blood circulation and the astringent property of this oil supports the contraction of blood vessels therefore lessening swelling, inflammation and irritation.
The anti-arthritic and warming property of this oil calms the nerves and soothes the muscles, making it an effective natural remedy for treating rheumatism, arthritis, muscular pain, sprains, inflamed joints and certain other problems due to improper blood circulation.
Massaging the painful area with a blend of few drops of Sugandha Kokila oil and Juniper oil along with soothing carrier oils like coconut oil can relieve tension in the muscles and foster blood circulation.
2. Relieves stress:
The essential oil extracted from the berries of Sugandha Kokila tree is an excellent tonic for the central nervous system. The relaxant properties of this oil supports in treating problems associated with stress and anxiety.
Tension headache, nervous tension, fear, insomnia, tiredness and lack of concentration can be managed at ease by using few drops of Sugandha Kokila oil in your warm bathing water or air freshener or to diffusers. Inhaling the comforting aroma of this oil clears your mind, increases your concentration power and grants you a sense of ultimate support.
3. Supports the digestive system:
The carminative, digestive and stomachic properties of this oil supports the digestive system and aids the process of metabolism. Massaging few drops of this oil blended with soothing carrier oils can assist one in relieving flatulence, promoting quick digestion and improving appetite. It can also be used as a bathing oil in a tub of warm water for assisting the functions of your digestive system.
4. Strengthens the entire system:
Sugandha Kokila oil increases the immune power and makes the body resistant against infections, microbes, harmful bacteria and other micro-organisms affecting its normal functioning. The antiseptic, anti-bacterial and antimicrobial properties of this oil help control infections like urinary infections and protect the system.
As an expectorant and decongestant, this oil is also beneficial to the respiratory system. It assists in breaking down and removing of excess mucus in the respiratory system. 2 to 3 drops of this oil can be added to your facial steam water for loosening the mucus.
5. Benefitting the chakras:
According to Ayurveda, Chakras are the transfer points for human feelings, emotions and functioning of certain endocrine glands. There are 7 chakras in a human body. Light Miller in her book ‘Ayurveda and Aromatherapy’ has said that “the essential oils increase the finest and farthest vibrations and assist all of the subtle bodies. Essential oils can stigmata and assist in the process of awakening, healing, opening the chakras, and strengthening the aura”.
Sugandha Kokila essential oil is said to benefit the 4th chakra-heart chakra dealing with absolute love for self and the divine, 2nd chakra-sacral chakra responsible for relationships, immune system, energy creation and sexual feelings and the 5th chakra-throat chakra accountable for integrity and speaking truth. Inhaling the aroma of this oil added to diffusers, vaporizers or burners can help you in strengthening your chakras.
Apart from these benefits, Sugandha Kokila oil is also used in making perfumes, incenses, scents, detergents, industrial fragrances and cosmetics.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to diagnose or replace any prescribed medication or professional advice. Do not use essential oils internally and consult your Ayurvedic practitioner before using it. Essential oils are highly concentrated so keep them out of reach of children.
Thought for the day:
The trees that are slow to grow bear the best fruit. -Moliere
Suggested Reading:
- Ayurveda in Nepal: Volume One: Ayurvedic Principles, Diagnosis and Treatment from Wasteland Press
- In Search of the Medicine Buddha: A Himalayan Journey by David Crow
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Essential Oils: The Complete Guide to the Use of Oils in Aromatherapy & Herbalism by Julia Lawless
Reference Links:
- Investigation of Nepalese Essential Oils. I. The Oil of Cinnamomum glaucescens (Sugandha Kokila)
- Sugandha Kokila oil by Everest Herbs
- Aromatherapy from Ayurveda’s Perspective by Yayoi Stavish


