 As nature’s immaculate coolant, the world celebrates Peppermint as the most distinguished member of the mint family, Labiatae along with Spearmint, Pennyroyal, Corsican mint, Lemon mint, Watermint, Lavender, Field mint, Apple mint or Chocolate mint, Patchouli, Thyme and Silver mint. Pliny the Elder (23-79 CE), the Roman natural philosopher, scientist and naturalist rightly said “The smell of mint stirs up the mind and appetite to a greedy desire of food.”
As nature’s immaculate coolant, the world celebrates Peppermint as the most distinguished member of the mint family, Labiatae along with Spearmint, Pennyroyal, Corsican mint, Lemon mint, Watermint, Lavender, Field mint, Apple mint or Chocolate mint, Patchouli, Thyme and Silver mint. Pliny the Elder (23-79 CE), the Roman natural philosopher, scientist and naturalist rightly said “The smell of mint stirs up the mind and appetite to a greedy desire of food.”
Peppermint essential oil is extracted from the aromatic leaves of this plant and is known since ages as an excellent digestive aid with a bundle of other health benefits as well. The encyclopedia of Ayurveda talks about the notable use of Peppermint essential oil as a cooling carminative that enhances digestion and elimination by eradicating blockages and facilitating the flow of energy from within.
Purchase Peppermint Essential Oil – Retail – CLICK HERE
Purchase Peppermint Essential Oil – Wholesale – CLICK HERE
Historical importance of Peppermint and its oil:
Peppermint dates back to 1000 BC when the dried leaves are said to be found in Pyramids. Indigenous to Europe, this herb was first used by the primeval Egyptians as a natural digestive support. Few mythological studies say that the word Peppermint has its origin from Greek myths in the outline of a love triangle involving Hades, his wife Persephone and the nymph Minthe (who was later turned into Peppermint).
Interestingly, Peppermint is a natural hybrid of Spearmint and Watermint. The ancient Romans loved growing Peppermint in their gardens and in the pathways of stepping stones for greeting their guests with its wonderful aroma and for its innumerable medicinal benefits.
It was also used as a form of currency for the kind of esteem and admiration it had in Egypt. Peppermint was used as a tooth polisher by the ancient monks.
The Biblical importance of Peppermint has added even more to its value. Jesus Christ says to the Pharisees, “But woe unto you, Pharisees! For ye tithe mint and rue and all manner of herbs, and pass over judgment and the love of God: these ought ye to have done, and not to leave the other undone.” It was also used as a culinary herb in the folklore cooking for seasoning meat and assisting in quicker digestion.
Listed as a natural remedy for treating all kinds of illnesses from venereal disease, cold, sores, headache and digestive problems, Peppermint emerged as a distinguished species in the London Pharmacopoeia in the 16th century. It was also mentioned in the Icelandic Pharmacopoeias as a much valued herbal remedy in 1240 AD. Peppermint was used as a prized herb by the Native Americans and now the United States is the world’s largest producer of Peppermint essential oil contributing to more than 75% of the total production.
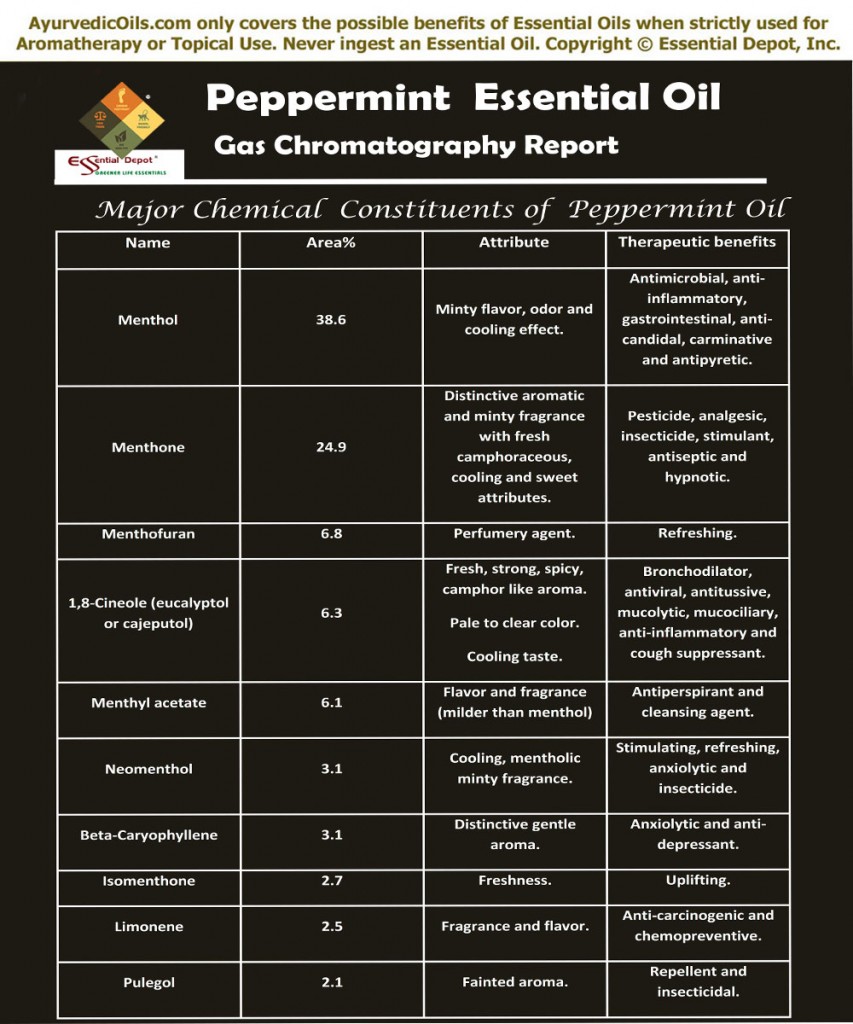
Chemical constituents Gas Chromatography Report of Peppermint essential oil:
According to the Gas chromatography report, Peppermint oil constitutes of 10 major chemical components that contribute to its distinctive fragrance, remedial properties and quality, among which, menthol has an upper hand with about 38.6 percent.
Just click on:
For learning more about the exclusive information of these key constituents of Peppermint oil.
The table below on the Gas Chromatography report talks about the principal chemical constituents and its role in granting the therapeutic properties and other attributes to Peppermint oil.
 Therapeutic properties of Peppermint essential oil:
Therapeutic properties of Peppermint essential oil:
The therapeutic actions of Peppermint essential oil are carminative, decongestant, immune stimulant, anti-infectious, febrifuge, cardio tonic, nervine, hypertensive, antipruritic, antifungal, sedative, expectorant, antibacterial, mucolytic and anti-carcinogenic.
Ayurvedic health benefits of Peppermint essential oil:
Known as Pudina in Sanskrit, Peppermint is a popular culinary herb used for its minty, fresh and enriching aroma for enhancing taste and adding extra flavor to the lip-smacking dishes. Ayurvedic remedies wholly depend on Mother Nature trusting that every single thing on the earth is an incredible part of nature including human beings.
The strong principles of Ayurveda establish that every individual is made up of three vital energy elements known as doshas (vata-air, pitta-fire and kapha-water), which determine the personality, character, behavior and health conditions of a person. A person is said to be healthy when there is perfect balance between all the three doshas and dosha imbalances cause illness. Peppermint and its essential oil in Ayurveda is said to calm all the three doshas.
Peppermint according to Ayurveda has cooling and heating energy (virya), sweet and pungent taste (rasa), dry, penetrating and light quality (guna), benefits the nerve, blood and plasma tissues (dhatu), with a post-digestive effect (vipaka), Peppermint stimulates the circulatory, nervous, digestive and respiratory channels (srotas).
Let’s have a look at the major Ayurvedic health benefits of Peppermint essential oil: 1. Keeps away from harmful bacteria and fungi:
1. Keeps away from harmful bacteria and fungi:
Peppermint is a powerful antibacterial oil mainly because of the presence of menthol that aids in fighting against harmful bacteria like salmonella, e.coli and staph.
A 2010 study on ‘Protective effects of bioactive phytochemicals from Mentha piperita with multiple health potentials’ proved that Peppermint oil has effective antimicrobial and antioxidant effect that fights against harmful microbes and supplemented for nutritional benefits and food preservation. Bacterial infections are responsible for wounds becoming septic and other skin problems like acne.
The Tehran University of Medical Sciences in Iran proved that the menthol component in Peppermint oil is defiant to fungus including candida. The State University of Brazil also established that Peppermint essential oil varieties have anti-candida effects. For all these reasons Peppermint oil acts as a natural remedy for treating fungal infections like athlete’s foot, ringworm, jock itch and other yeast infections.
Applying 2 drops of Peppermint essential oil blended with gentle carrier oils like coconut oil aids in treating bacterial and fungal infections. You can also add 2 drops of this oil in warm foot bath or in bathing water for fighting against such detrimental microbes.
2. Enlivens the mind:
The invigorating, refreshing, cooling and reassuring aroma of Peppermint essential oil boosts mental power. Inhaling the aroma of this oil grants a complete stream of freshness to fight the challenges of a rising day.
Adding 2 to 3 drops of drops of Peppermint oil in your air freshener, diffuser or in your handkerchief can grant you immense energy and confidence throughout the day. This therapy employed in your study room can help improve your memory skills and concentration power.
3 to 4 drops of Peppermint oil blended with Sesame oil can act as an efficacious massage oil and as a bathing oil for enhancing your mental strength, treating stress, reducing fatigue and anxiety. It also helps in treating anger, mental strain, confusion, nervousness, palpitations, vertigo and depression.
3. Alleviates tension headache better than the other alternative therapies:
Peppermint essential oil is also an effectual natural remedy for treating tension headache. A clinical trial on ‘Effectiveness of Oleum menthae piperitae and paracetamol in therapy of headache of the tension type’ witnessed “Peppermint oil thus proves to be a well-tolerated and cost-effective alternative to usual therapies for alleviating tension-type headache.” This study also proved that there was not much significant difference in efficacy between acetaminophen and Peppermint oil and there are no reported adverse effects as well.
4. Clears all kinds of stagnation:
Peppermint essential oil is a proven stimulant and tonic especially to the brain, pancreas and heart. It is known for clearing away all kinds of stagnations including physical and mental. Peppermint oil clears stagnation in the blood, lymph, stomach and gallbladder. It also breaks emotional blockages.
The expectorant and decongestant properties of this oil help in open the blocked sinus passages and aid in clearing mucus deposits from the respiratory tract by adding 2 drops of this oil in steam inhalation.
The diaphoretic quality of Peppermint oil aids in reducing the body temperature in the early stages of fever by releasing the heat of the body through sweat. Applying two drops of Peppermint oil blended with coconut oil on your foot helps in quicker recovery from fever. This blend can also be rubbed on the chest, back and neck for treating congestion, cough and blocked nose.
5. Stimulates the digestive system:
The essential oil of Peppermint and the herb itself are known to the world as a promising digestive remedy. Numerous research studies have proved that Peppermint oil is effective in relaxing gastrointestinal smooth muscle, more or less due the antagonistic effect on calcium channels in the gut.
The American Family Physician Forum states that Peppermint oil is effective in treating irritable bowel syndrome symptoms, non-ulcer dyspepsia, tension headache and lessening spasm at the time of gastrointestinal procedures.
Peppermint oil along with the combination of caraway oil has been proved in reducing the symptoms of non-ulcer dyspepsia like bloating, fullness and gastro-intestinal spasm. Gently rub 3 drops of Peppermint essential oil with Sesame oil on the stomach and abdomen to help relieve indigestion, nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, constipation and pain.
6. Absolute care for hair and skin:
The skin-friendly attributes of Peppermint oil aids in treating eczema, lesions, acne, insect bites, rashes, allergies, irritation and itchiness. Gently massaging your skin with 2 drops of Peppermint oil blended with sweet almond oil helps in nourishing and hydrating dry, dull and lifeless skin. You can also add 2 to 3 drops of oil in your daily lotions and creams and apply it on the affected area.
Dandruff, dry itchy scalp and lice are the major problems associated with hair. Peppermint oil has stimulating and cooling effects. When added to sesame oil and massaged on the scalp helps improve blood circulation, enrich the scalp, conditions your hair and improves hair growth. Adding 3 to 4 drops of Peppermint oil to your shampoo or hair conditioner can add shine to your hair and make it look smooth and silky.
Other health benefits:
Few believe that adding 1 drop of Peppermint oil besides your pillow can bring dreams that reflect your future. Peppermint essential oil when used in massage, added to diffuser or diluted in bath can help relieve menstrual cramps, muscular pain, urinary infections, belching, nerve pain, uterine spasms and much more. The presence of menthol makes Peppermint, a much valued oil in making toothpastes, mouthwashes, cough syrups, ointments, shampoos and soaps, vaporizing rubs etc.
Disclaimer: Never use essential oils internally or apply directly on skin as essential oils are highly concentrated liquids. Always remember using essential oils blended with carrier oils or diluted in bath or in diffusers. Speak with your Ayurvedic Practitioner before using essential oils for your specific body type and your unique state of health.
The MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) of Peppermint oil is readily available for your enhanced safety and better usage.
Gas Chromatography Report of Peppermint essential oil.
Thought for the day:
The world is like a little marsh filled with mint and white hawthorn.
-Mary MacLane
Suggested Reading:
- HEALING POWERS OF PEPPERMINT OIL (The Aromatherapy Professional: Healing with Essential Oils) by KG Stiles
- How to Use Peppermint Essential Oil (Aromatherapy) by Miriam Kinai
- Digestive Wellness: Strengthen the Immune System and Prevent Disease Through Healthy Digestion, Fourth Edition by Elizabeth Lipski
- Integrative Gastroenterology (Weil Integrative Medicine Library) by Gerard Mullin
Reference Links:
- Peppermint History by Indepthinfo on Peppermint
- Peppermint Oil by American Family Physician
- Protective effects of bioactive phytochemicals from Mentha piperita with multiple health potentials by Shahed University, Tehran published in PubMed
- Effectiveness of Oleum menthae piperitae and paracetamol in therapy of headache of the tension type, published in PubMed



